The assignment of this week was to measure the power consumption of an output device. We used a gear box motor.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | A Power Supply machine is a device that provides electrical power to other devices. It is used to give a specific voltage and test electronic devices. |
| Voltage (V) | The push that drives electricity through a circuit. For example, when a motor is said to run on 12V it means it needs a push of 12 volts to operate properly. |
| Current (A) | The flow of electricity, how much electricity is actually moving through. For example, a motor that says 0.5A means it needs a flow of 0.5 amps when running normally. |
| Multimeter | A tool used to measure electrical values (V, A, resistance, continuity, diode test). |
This is what the screen of the power supply looks like and this is where we control the Voltage and Current. Spinning coarse moves numbers faster and fine slower and more precise.

We check the motor's label to see what values to use for V and A. Datasheets of devices include this information. It is important to set a limit to avoid problems. For example, when LEDs light up they heat up, and as they heat up they end up pulling more and more current which would eventually lead to them burning out. Setting a limit on the amount of current prevents this.
For the motor we are using we needed a Voltage of 12V.

To set the current we first turned the machine off and created a short circuit, making the red and black test leads touch. After this we turned the machine back on and set the A to 0.5.
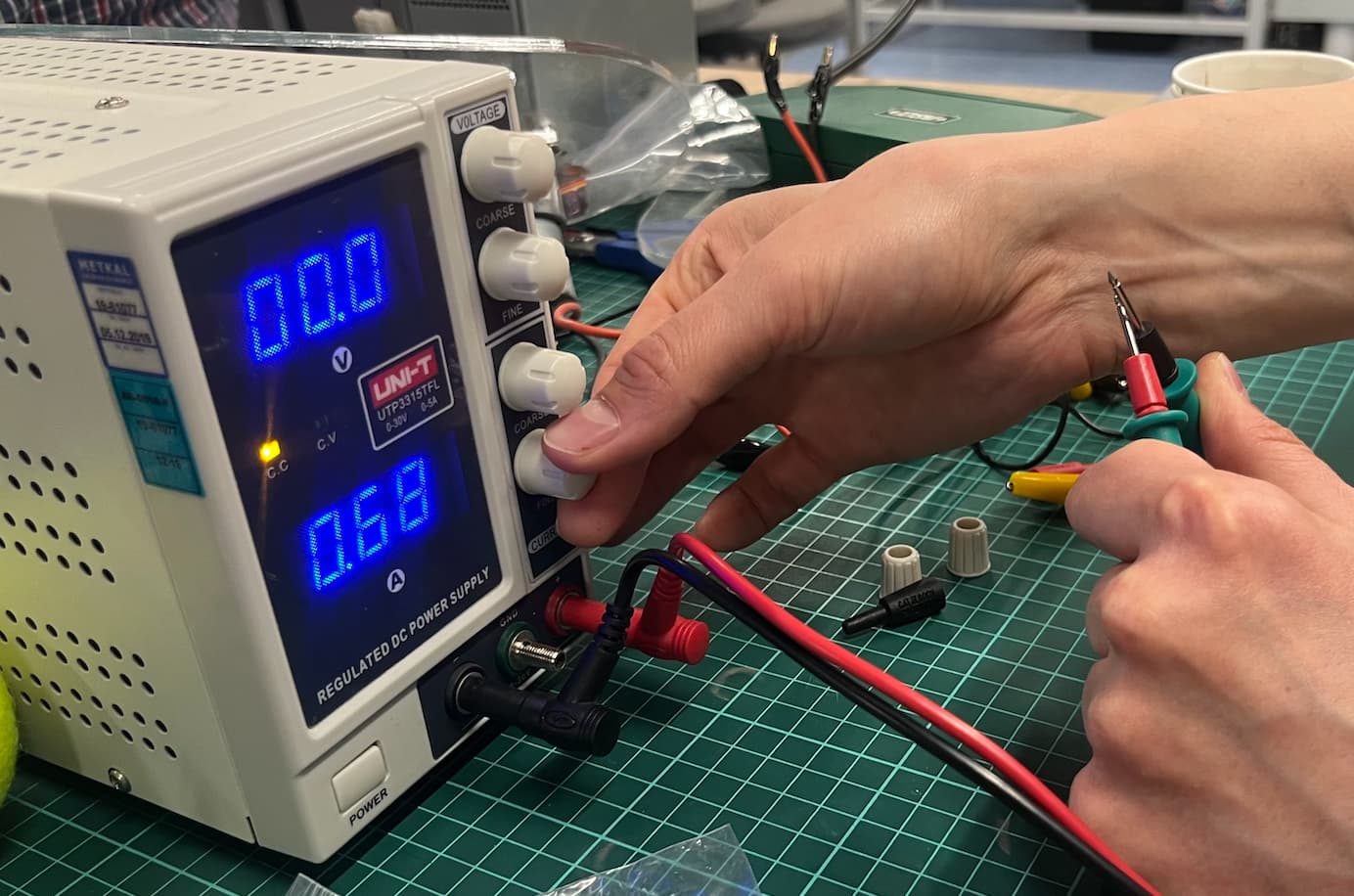
This powered on the motor, causing it to spin.
A multimeter can be used with a power supply for more precise measuring. The power supply both measures and supplies power, while the multimeter only measures. Here is the setup we used and the results we got on the multimeter.
We then applied pressure to the motor, making it harder for it to spin and therefore needing more energy. This required more power consumption as shown.